CAMERA WORK:
-Wide shot. Show a wide view of the scene.

- Close-up shot. Show someone from shoulders up.

- Master shot. Show were characters/ objects are positioned in a scene.

- Aerial shot. Filmed from the air.

- Over the shoulder shot. Just what it says.

-Two-shot. Show two people.

- Long shot. Show someone from head to toes.

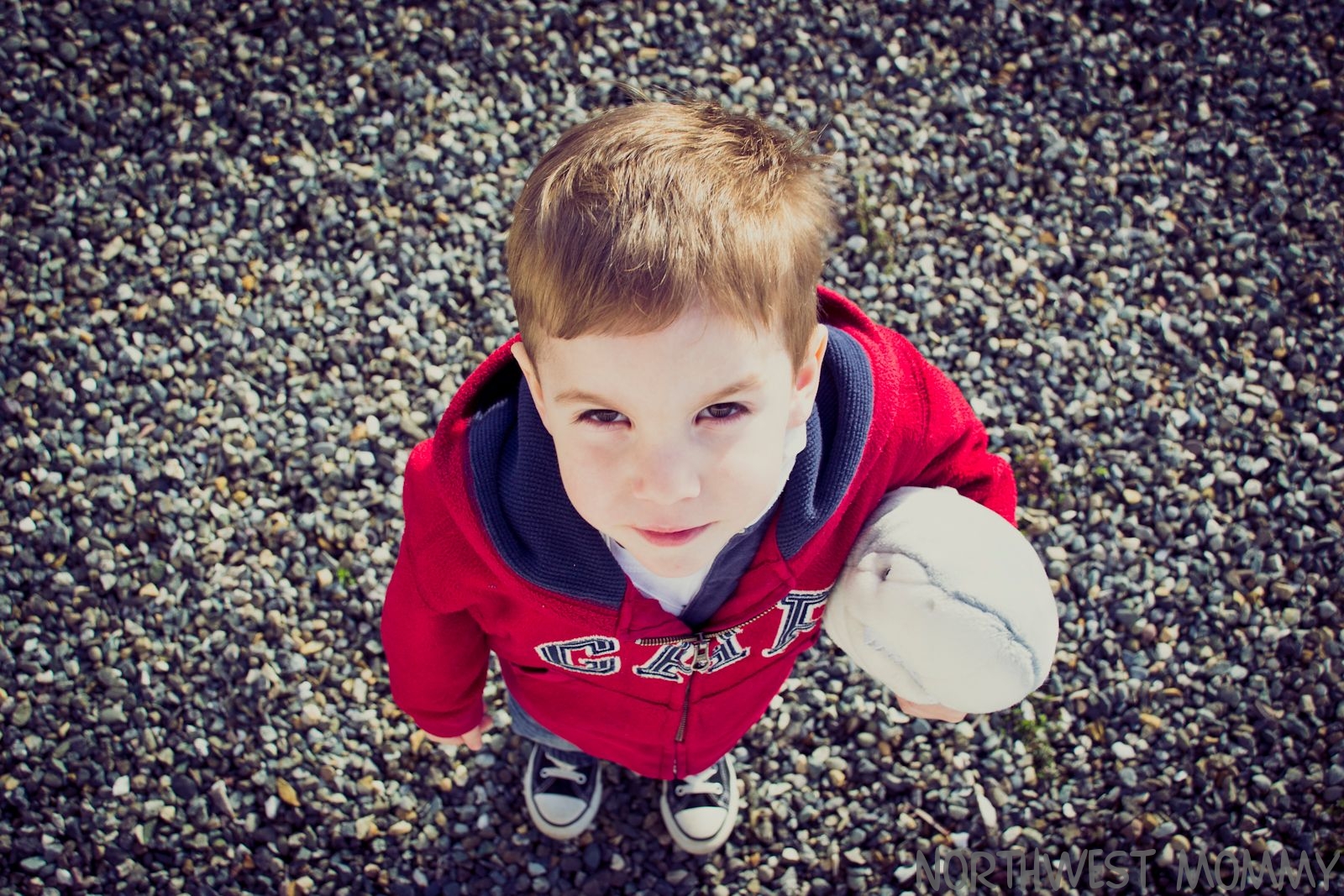
- High angle. Camera looks down on someone showing inferiority.

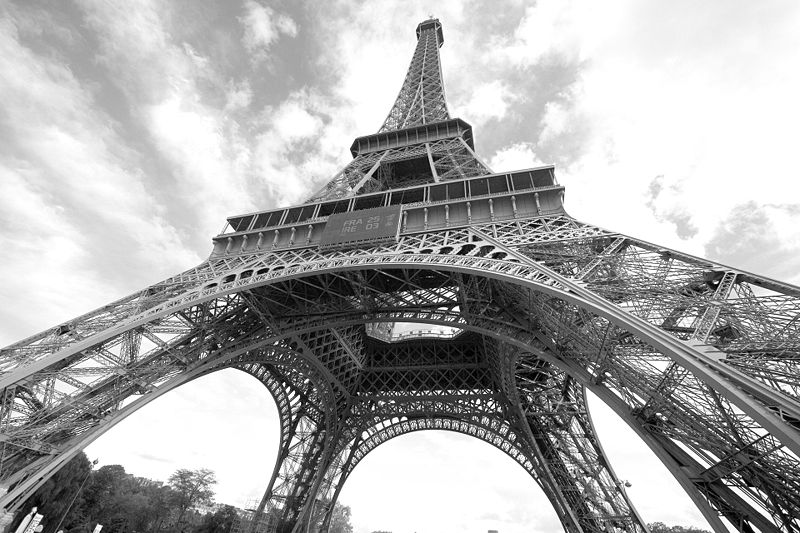
- Low angle. Camera looks up at someone showing superiority.

- Canted angle. Camera at a slanted angle.

Movemets:
- Pan. Moves from side to side.
-Tilt. The camera moves up and down.
-Track. Follows a person or an object.
- Crane. Moves up or down on a crane.
- Steadicam. Creates a gliding effect.
- Zoom. In or out.
- Reverse zoom. Out or in.
EDITTING TECHNIQUES:
- Shot-reverse-shot. Back and forth between people in a conversation.

- Action match. Cutting to show another angle of the scene.

- Crosscutting. Show two actions happening simultaneously.
- Slow motion. Just what it says.
- Graphic match. Similar shape or colour.

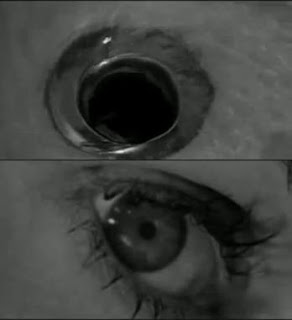
- Eyeline match. Showing first a person looking something and the next scene is the object the person was looking at.

- Superimposition. Just what it says.

Today i am going to talk about MISE-EN-SCENE.
-Location. Where the scene takes place. In this image we can see that the location is a normal bathroom.

-Set design. How the setting is designed.
-Custome. Clothes worn by the actors. In this image we can appreciate that the custome of this actor is a famous superhero (superman).

-Make-up. Just what it said.
-Props. Objects used in the scene. In this image we can see that the props are the head of the animals.

-High key lighting. Bright lighting.

-Low key lighting. Dark lighting.